Cheng RZ (2020) COVID-19 highlights the shortcomings of evidence-based medicine.
The Spanish Flu of ~100 years ago took over the world and infected one third of the world’s population (~500 million people) worldwide, and killed ~50 million (~3% of the world’s population). Most of us probably didn’t know or didn’t care much about the Spanish Flu until Covid-19. With today’s advanced hygiene, economy and technology compared to a century ago, most of us probably thought pandemics of that scale are long gone. Well, I did.
What a shock, here we are, ~10 months later, we are still immersed in the Covid-19 panic and chaos, with >1 million people killed and trillions of dollars lost. The world is still in a locked down mode, many people, if not affected by Covid-19 directly, are most definitely affected by the hardship due to lock-down.
Since the Spanish flu, the world has seen many epidemics and pandemics, but none at the scale of Covid-19. One would expect that the leadership in our public health systems, the medical establishment and worldwide governments have learned how to deal with such a public health hazard. Needless to say, we all have been sadly disappointed, particularly at the responses from the leadership in the public health and the medical establishment.
Covid-19 provided a litmus test for the politicians, their top medical advisors, leaders in various industries including social media and other societal activists. I am sure many global citizens share with me the view that most of them have failed us miserably in this Covid-19 global fight!
Covid-19 is a major crisis, but it also presents a great opportunity. In Chinese, crisis is translated into 危機, which is consisted of 2 characters, Danger (危) and Opportunity (機). Great disasters often call for deep reflections and soul searching, which may bring about great reforms. We, the global villagers (the consumers, the healthcare professionals, industrial leaders and the politicians), all need to reflect on Covod-19: what we have done right, and what we have done wrong and how could we improve in the management of Covid-19 down the road and future public disasters. Yes, Covid-19 won’t be the last one, epidemics and pandemics are on the rise1.
Digging deeper, Covid-19 is revealing more problems in our current medical system, “Evidence-Based Medicine” (EBM), than just a catastrophic pandemic!
In this article I’ll discuss briefly some key problems in EBM, followed by a summary review of the common pathological features of viral infections including those of Covid-19, to point out the key underlying biochemical and pathological mechanism: disturbance in redox homeostasis, concluding with an analysis of redox therapy including antioxidants such as vitamin C in Covid-19 intervention.
Shortcomings of Evidence-Based Medicine, revealed in Covid-19 management
One of the major problems of EBM is the gradually increasing bias in what constitutes as “evidence” in EBM. Another is the lack or insignificant role of mechanistic reasoning, or lack of “logical reasoning” in EBM. The third is what I consider as the “Nobel Prize Mentality” dominance in today’s clinical medicine, i.e., using the narrowly focused basic science research principles and tools to address complex and holistic clinical problems. The management (or better mismanagement) of Covid-19 illustrates these problems. The mismanagement is causing more problems than the problems directly due to Covid-19 per se.
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) movement, started in the 1990s, has gradually become the central dogma of today’s medical practice. Of course, this doesn’t mean the medicine practiced in the past thousands of years is not evidence based. Even today, ~50% of what a clinician does in the clinic is still so-called empirical medicine (or experience based), despite the dominance of EBM. Medicine practiced in the past thousands of years, if not longer, has always been “evidence” based. The key question here is what is considered as evidence.
What is Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM)?
Evidence-based medicine is interpreted as the integration of best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values2. EBM aims for the ideal that healthcare professionals should make conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in their everyday practice”2.
Randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) are only part of the evidence in EBM. There are several levels of evidence in EBM.
There is no doubt that evidence is important. The center of EBM is “evidence”. There are generally 4 different levels of evidence, from RCTs to case studies to clinical expert experience (empirical)3. It’s clear here that, although RCTs have the highest weight in “evidence”, RCTs are not the only evidence in EBM. However, all the scientists and medical doctors whom I know and have communicated with view RCT as the only evidence. They seem to think that if there is no RCT data, then it’s not EBM. They have no idea that EBM has several levels of evidence. To be honest, I didn’t know what EMB exactly is either until I looked it up in the literature. I venture to say that this is quite common among scientists and clinicians.
Another major problem of EBM is the lack of clinical or mechanistic reasoning. RCT results and treatment guidelines contain limitations and financial conflicts which may result in bias. We clinicians must still reason through the best choices for an individual patient even in the absence of full and secure knowledge4, as is in this Covid-19 pandemic. Covid-19 is a new disease, but it doesn’t mean we knew nothing in the treatment and prevention of Covid-19. Even without thorough research, there is plenty we already know about viral infections, Covid-19 included, that we can apply in prevention and treatment.
Disturbingly increasing trend of biased “Evidence” favorable to for-profit patentable drugs in EBM.
Publicly funded RCTs have been declining, while for-profit industry funded RCTs are on the rise, a trend with a deep and potentially biased and unfair influence on our healthcare policy, with potentially grave consequences.
There is no doubt that RCTs are important. Well-designed RCT results are considered the strongest evidence in EBM. But RCTs are very costly and are becoming more and more limited to organizations with strong financial backings. A 2015 Johns Hopkins University study found the number of clinical trials funded by for-profit industry increased 43% while those funded by the NIH decreased by 24%, between 2006 and 20145. While the goals of NIH-funded RCTs are not to make a profit on the market, the for-profit industry funded RCTs are clearly for profit.
There is no doubt that lifestyle and nutrition play fundamentally important roles in our health maintenance and disease prevention and treatment. However, lifestyle and nutrition research results are usually not patentable. There is no financial incentive in doing RCTs by for-profit industry, leading to a bias towards low representation of lifestyle and nutrition medicine in the “evidence database” that EBM relies on. But can anyone tell me that lifestyle and nutrition medicine is not important?
With a growing dominance of for-profit industry sponsored RCTs making up the “best evidence” in EBM, no wonder, medical practice today is biased and heavily influenced by the big pharma.
Some other facts:
- For profit Industry doesn’t fund trials most important for public health due to lack of financial incentive.6 This includes the lifestyle and nutrition medicine discussed above.
- The Johns Hopkins University’s Comprehensive Cancer Center found conflicts of interest in more than one-third of 1,500 cancer studies published in prominent medical journals in 20066.
- As many as 70% of approved drugs are not new drugs, wasting billions of dollars of unnecessary clinical trials.7
Today’s clinical medicine has been dominated by the basic science mentality (“Nobel-prize mentality”).
Nobel prize is the crown jewel that attracts the top medical and biological scientists. Those who reach the top of various medical specialties have spent most of their careers in basic research. There is a dichotomy between those who lead in medicine and those who actually practice medicine. Those influential medical experts, who write “disease management guidelines” and influence healthcare policies, are mostly attracted and dominated by the “Nobel-prize mentality”. This disturbing trend is partly illustrated in the gradual decrease of Nobel prizes awarded to clinicians over the past 100 years (Fig. 1).
The proportion of clinicians to win Nobel prize in physiology and medicine have been steadily declining over the past 100+ years, from 65%-90% ~100 years ago to a merely ~20% in the 21st century.8 While basic research is important, only ~1% of the highly promising basic research is translated into clinical medical practice.9 Today’s Nobel prizes may not be what Mr. Alfred Nobel intended in his will. The Nobel committee over 100 years ago interpreted Mr. Nobel’s will as: “the domain of physiology or medicine” was understood to encompass the theoretical as well as the practical medical sciences8,10.
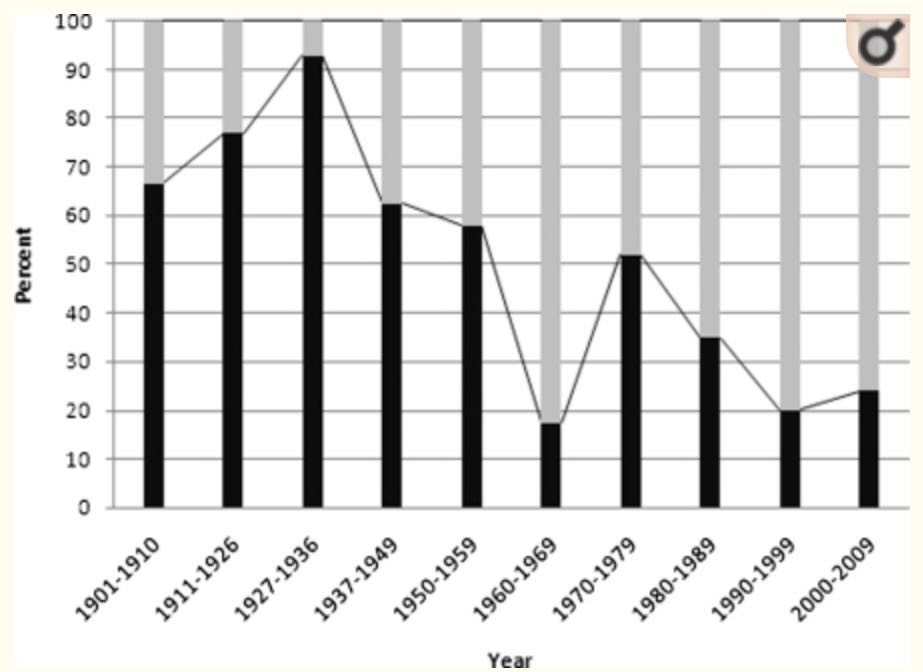 Fig. 1. Nobel Prizes in medicine: are clinicians out of fashion? Source: Ashrafian, H., Patel, V. M., Skapinakis, P. & Athanasiou, T. J R Soc Med 104, 387–389 (2011).
Fig. 1. Nobel Prizes in medicine: are clinicians out of fashion? Source: Ashrafian, H., Patel, V. M., Skapinakis, P. & Athanasiou, T. J R Soc Med 104, 387–389 (2011).
The approaches to clinical medicine and to basic medical research are and should be different. Basic research is to dissect complex problems into smaller and unit level questions, often looking at a particular molecule or a mechanism, irrespective of the whole system, and try to find answers. Whereas clinical medicine should teach how to integrate knowledge learned from various aspects into one holistic treatment plan for a particular patient. Clinical medicine should view a patient as a whole, trying to understand not only the clinical manifestations, but also the root causes as well as the processes connecting the root causes and the clinical presentations (Fig. 2). Only when we address the root causes, the disease processes and the clinical manifestations, the it becomes possible for us to cure the patients.
All diseases have their root causes, which, via certain pathological mechanisms or processes, lead to clinical signs and symptoms (Fig. 2). Research into disease root causes and management are usually not patentable, whereas specific agents (drugs) to manipulate pathological mechanisms are. As a result, the medical literature is full of research papers studying the biological processes, which may lead to new drug discoveries and handsome financial rewards. But we know clearly, interfering only at the mechanism level, not at the root cause level, is only part of a disease management plan, not a complete solution. But this is what medicine is teaching our doctors today: one or a few drugs based, incomplete treatment plan, without addressing the root causes of diseases. As a result, although the market is full of redundant drugs for common chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus and hypertension, none of these chronic diseases are curable with these existing drugs. More and more clinical research shows that chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension are reversible with lifestyle changes including dietary changes11–14. We have helped numerous diabetic or hypertensive patients to go off their drugs in our clinics with this integrative approach. This simple logic, unfortunately, is forgotten and not mentioned in today’s medicine.
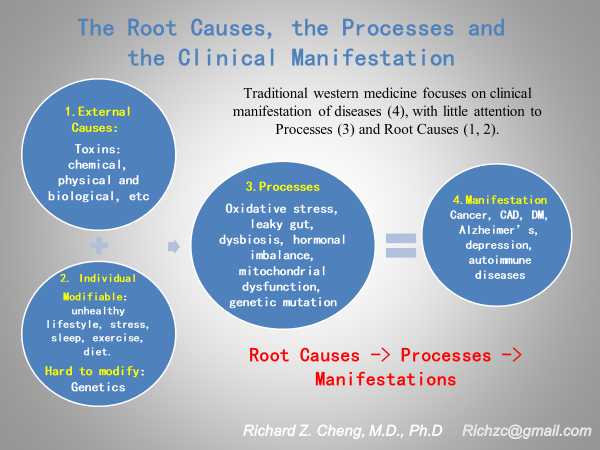
Fig. 2. The root causes, processes and clinical manifestations of diseases.
Disturbance of redox homeostasis, or increased oxidative stress, is the key underlying pathology of viral infections, including Covid-19.
A common feature of many viral infections, including the upper and lower respiratory infections caused by respiratory viruses is the disturbance of redox homeostasis, or increased oxidative stress. Redox homeostasis describes the balance between the production of reactive oxygen or nitrogen species (ROS, RNS, respectively, or RONS, collectively) and their scavenging. Redox biology plays a critical role in various cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, signaling, and metabolism. Redox homeostasis and the disturbance thereof plays an important role in pathology and may lead to oxidative stress, chronic activation of immune responses, and inflammation15,16. Chronic elevation of ROS may lead to oxidizing damages to DNAs, proteins, lipids and resulting in dysfunction of organelles and apoptosis17.
The group of viruses that may cause respiratory infections include influenza, human respiratory syncytial, human rhino, human metapneumo, parainfluenza, adeno and coronaviruses (SARS-Cov), the latter includes the virus responsible for Covid-19, SARS-Cov-2, a new member of the coronaviruses.
A large body of evidence exists in the literature that demonstrates the correlation between the significant increase in ROS and most, if not all, viral respiratory infections18. Moreover, elevated ROS is not only a feature of respiratory infections, but is also present in other viral infections such as hepatitis B, C and many others. Covid-19 is no exception. Early research shows SARS-Cov-2 infection, Covid-19, is associated with significantly increased oxidative stress, often described as “cytokine storm”.
Key pathologies of Covid-19 and mechanisms of vitamin C in the treatment of viral infections.
“Cytokine storm” or significant oxidative stress plays a significant role in Covid-19 pathology. Oxidative stress is actually a common mechanism in many viral infections. Vitamin C is a prototypical antioxidant. Vitamin C’s powerful antioxidant effect probably explains the clinical improvement observed in pneumonia, sepsis and respiratory distress19–22.
A review of worldwide reactions to and the management of Covid-19 reveals a few severe problems.
- Covid-19 management worldwide has been severely politicized. This is reflected both internationally and domestically. Covid-19 pandemic is a huge challenge to the mankind and we, of all nations and races, should have united to face the common enemy. But instead, international and domestic politics have mostly hijacked this public health crisis and caused unnecessary chaos and mismanagement with severe consequences.
- The medical advisors to governments worldwide including WHO have been providing incomplete medical advises which may have been misleading to government leaders. These public health officials carry the major responsibility of assessing and analyzing the pandemic problem, reviewing the knowledge we learned in the past and synthesizing comprehensive (and contingency) plans to combat the pandemic. However, the responses from the public health officials we have seen worldwide have been incomplete and disappointing. This probably reflects much deeper problems rooted in the contemporary medicine.
What have the public health officials, top medical agencies and advisors and governments done worldwide to fight Covid-19 pandemic? What we have seen and heard mostly is nothing but a lot of fighting, arguments and expectation of vaccines, especially in the US. I don’t hear any of these top experts or medical agencies talk about prevention, particularly nutritional importance in prevention and treatment of Cvoid-19. Our health depends on nutrition. This is simply logical and a common sense. In the absence of specific “anti-Covid” drugs, our own immunity is all we have to hold the virus at bay. Even with specific drugs, our immunity still plays a major role in disease fighting. But why don’t we hear much about it? Why don’t the top experts recommend it? It’s too “low tech”? Many conscientious healthcare professionals and others stand out and promote healthy lifestyle and nutrition to prevent Covid-19 or fight against it once one gets it, including vitamin C and vitamin D. Dr. Anthony Fauci, the top medical advisor to the Trump Administration, is reportedly taking vitamins C and D privately, but I never heard him recommending it publicly23. Are vitamins C and D good enough for him, but not good for the public? Not only didn’t we hear these public recommendations, those science based nutritional recommendations, like the ones Dr. Fauci was taking, have been mostly censored by the major media. I am one of the victims of the censorship.
When faced with the common enemy, Covid-19 pandemic, we should have united to fight against it. But we all have been sourly disappointed and felt betrayed by those politicians, top medical experts and the media as well. Some of these interest groups have hijacked this global tragedy for their hidden agenda. I have never seen medicine to be so politicized in my 40 plus years in medicine.
I came across Dr. Linus Pauling’s work on vitamin C 20 some years ago. In recent years, I spent more time researching vitamin C. I was amazed that as a tiny molecule, vitamin C has a wide variety of biological effects on nearly every aspect of our life, including, but not limited to, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and as an essential cofactor in collagen synthesis24,25. You may be surprised to learn that vitamin C even plays a critical role on your mood.26 Most people probably don’t really realize the importance of collagen in our body. But we won’t discuss that here. What’s relevant to Covid-19 pandemic is vitamin C’s antimicrobial and antioxidant effects.
The ignorance or suppression of vitamin C reflects the lack of logic or “common sense” in mainstream medicine.
- Vitamin C can prevent and improve pneumonia.
A meta-analysis of 148 animal studies show that vitamin C can alleviate or prevent bacterial, viral and protozoan infections. Vitamin C cuts the risks of colds by 50% in physically active adults. Two randomized and controlled studies (RCT) show a dose-dependent response in the therapeutic effects of vitamin C in common colds. Three RCTs demonstrate that vitamin C can prevent pneumonia and 2 RCTs show vitamin C can improve pneumonia treatment. One RCT shows vitamin C is beneficial in the treatment of tetanus27.
- High dose intravenous vitamin C (HDIVC) shortens mechanical ventilation.
HDIVC improves severe pneumonia patients. A recent meta-analysis pooled the data from 9 qualified clinical trials and found strong evidence that high dose IV vitamin C shortens patient time on mechanical ventilation by 14-25% with only relatively small vitamin C doses (1,000 mg – 6,000 mg)28.
- HDIVC reduces mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and in Covid-19 patients
In a clinical trial of 32 ARDS patients, HDIVC (1,000 mg + N-acetyl cysteine + selenium + vitamin E, every 6 hours IV) showed a 47% reduction in mortality rate compared to the 71% mortality rate in the control group29. Another recent study of 96 septic patients with HDIVC (6,000 mg of vitamin C + hydrocortisone + thiamine, every 6 hours IV) cut the mortality rate by ~32%30. HDIVC for the treatment of Covid-19 was first reported in China. In a clinical study of 54 severe to critically ill Covid-19 patients shows HDIVC (24,000 mg/24 hours IV) reduced 28-day mortality and significant improvement of oxygenation and inflammatory status31. In a separate clinical series study of 12 severe and critical Covid-19 patients, HDIVC showed significant clinical oxygenation improvement with reduction in inflammatory markers and organ failure (SOFA) score31.
- Oral high dose vitamin C can prevent common cold.
Several studies in the past have shown that vitamin C prevents common cold and reduces the disease severity once catching the cold including one earlier this year, a randomized controlled trial of 1444 young army recruits. This Korean study showed that vitamin C at doses as high as 6,000 mg daily reduced the odds of developing common cold32.
- Vitamin C deficiency is more common than we realized, both in sick patients and in the general population.
Vitamin C deficiency is common among patients with acute and chronic diseases. 40% of ICU patients with septic shock have blood levels of vitamin C near zero, diagnostic of scurvy (Vit C < 11 umol/L), with the remainder of ICU patients have hypovitaminosis C (Vit C < 23 umol/L). ~50% of non-septic ICU patients also show hypovitaminosis C33. Low plasma vitamin C levels are associated with more severe organ failure and increased mortality34,35. Hypovitaminosis C is relatively common in Western populations and vitamin C deficiency (VC < 11 umol/L) is the 4th leading nutrient deficiency in the US33. The 2007-2010 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey of approximately 16,000 children and adults found that almost 40% had low levels of vitamin C, while 88% of the U.S. population did not meet the daily requirement for vitamin E (noted to enhance the effects of vitamin C)36.
- Covid-19 patients have undetectable or very low blood levels of Undetectable Vitamin C.
Vitamin C was not detectable in 17 out of 18 Covid-19 patients with ARDS, a Spanish study reports, with the remaining patient showing very low blood vitamin C level37.
- Vitamin C is safe and is without significant side effects, even at very high doses.
An NIH expert panel consensus document (updated in February 2020) clearly states that HDIVC is safe even at very high doses38. Early clinical studies show HDIVC is highly promising in Covid-19 treatment1,19,38–40. Based on these and their clinical experience of HDIVC, the governments of Shanghai and Guangdong officially included HDIVC in their Covid-19 treatment protocols41,42. The science and rationale for HDIVC in treatment of Covid-19 were reviewed and presented in my NIH guest speech43. These early Chinese experiences in HDIVC on Covid-19 caused worldwide interest which was in part kicked off by my new associates at ITM Ltd. and The First Dragon Foundation™ Ltd. (In organization) who issued a global release44 that also included introduction to the New USA Federal “Right to Try Act”: According to the peer-reviewed Orthomolecular Medicine News Service, vitamin IVs can be arranged in virtually any hospital, anywhere in the world, and the new federal “Right to Try Act” gives patients the power to demand IV vitamin C treatment45.
Are vaccines the answer to the Covid-19 pandemic?
As I clearly stated previously, it’s clear that the epidemics and pandemics are on the rise1. Covid-19 is just a wake-up call. Due to the nature of vaccine research and development, there is always a significant delay between the outbreak of an epidemic and the clinical wide availability of effective vaccines. Eight months into the Covid-19 pandemic, there is still no SARS-Cov-2 specific vaccines available. And yet, the only universally accepted and recommended “miracle” that nearly all governments worldwide are hoping is a magic vaccine(s). Clearly this “vaccine” only Covid-19 strategy is incomplete. An integrative approach is clearly indicated to include healthy lifestyle with sufficient nutrition, esp. vitamins C, D and minerals like magnesium and zinc1,46.
Protected Population Immunity with vitamin C and other nutrients and healthy lifestyle should be part of the integral strategy to the prevention and treatment of Coivd-19 and future such epidemics1.
Where is “common sense” in evidence-based medicine?
Various organizations, doctors and citizens alike worldwide have been calling for their local and national governments on vitamin C’s potential effects on Covid-19. Some conscientious doctors at the highest level of the US department of Health and Human Services have also tried to call attention to vitamin C. It should be plain common sense to try HDIVC in Covid-19 treatment. The FDA even allows “compassionate drug use” which stipulates the use of new and unapproved drug to treat seriously ill patient when no other treatments are available47.
An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure, as the old saying goes. Have those top medical advisors (and medical agencies) forgotten the old wisdom? Why are they so much against antiviral nutrients such as vitamin C and vitamin D?
In summary, vitamin C, taken both orally or intravenously, is very safe and is effective in the prevention and treatment of both mild and severe viral infections. There is nothing to lose, but a lot to gain with vitamin C use in Coivd-19. But why such great remedies are being suppressed?
Another problem that Covid-19 has highlighted is that the medical establishment views Covid-19 as a totally new disease and ignores what we learned from the previous research on viruses and disease. Yes, Covid-19 is a brand-new disease caused by a brand-new virus, SARS-Cov-2 virus. However, many viral infections, particularly the family of coronaviruses including the viral agents that caused 2003 SARS pandemic and MERS pandemic in 2013, and Covid-19 now share much in common, particularly the significantly elevated oxidative stress (or cytokine storm)1,19. Most, if not all, of the pathologies seen in Covid-19 can be traced to the oxidative damages induced by SARS-Cov-2. This is the rationale for why antioxidants have shown promising results in the treatment of Covid-19 including HDIVC, vitamin C being a prototypical antioxidant.
The current medical system views diseases at from their symptoms and often fails to recognize their root causes and common biological features and pathways. Of course, this view of diseases is conveniently compatible with the needs of the medical establishment for publications and research grants: more diseases, more research grants and more research dollars. This view is also conveniently compatible with the pharmaceutical interests where more drugs can be developed and more drug sales. Of course, all these are at the expense of consumers and their health. This scenario is common in the management of most chronic diseases. Top diabetes experts are very eloquent on the complicated mechanisms of antidiabetic drugs when a simple measure of significantly reducing the carbohydrates in the diet along with supplements of essential nutrients could return blood sugar to normal levels.
Evidence based medicine is the main school of thought that guides the clinical medicine today. A review of the definition of EBM finds the lack of logics or “common sense” having any place in EBM2,3. What’s presented in this article makes it quite clear that there is a lack of common sense in EBM and that vitamin C should have a place in the treatment of Covi-19 pandemic.
Many consumers and healthcare professionals may not realize these problems ordinarily, but now with the outbreak of Covid-19, and huge losses in lives and economies with nearly everyone in every corner of the world affected, this distorted and incomplete view of diseases by the medical establishment should serve as a wake-up call to all of us, healthcare professionals and consumers alike. Many lives could have been saved. Many lives would be saved should the governments start incorporating HDIVC into the Covid-19 fight, just like Shanghai and Guangdong did. Entire cities don’t have to be locked down. The economy can be revived more rapidly.
But are they listening?
References
- Richard Z. Cheng. Protected Population Immunity, Not A Vaccine, Is The Way To Stop Covid-19 Pandemic. J Clin Immunol Immunother 6, 1–4 (2020).
- Hines, K. Evidence-Based Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/gim/research/method/ebm.html.
- Tenny, S. & Varacallo, M. Evidence Based Medicine (EBM). in StatPearls (StatPearls Publishing, 2020).
- Sniderman, A. D., LaChapelle, K. J., Rachon, N. A. & Furberg, C. D. The necessity for clinical reasoning in the era of evidence-based medicine. Mayo Clin. Proc. 88, 1108–1114 (2013).
- Ehrhardt, S., Appel, L. J. & Meinert, C. L. Trends in National Institutes of Health Funding for Clinical Trials Registered in ClinicalTrials.gov. JAMA 314, 2566–2567 (2015).
- Cohn, M. Industry funds six times more clinical trials than feds, research shows – Baltimore Sun. https://www.baltimoresun.com/health/bs-hs-trial-funding-20151214-story.html (2015).
- Boston, 677 Huntington Avenue & Ma 02115 +1495‑1000. Remove the For-Profit Variable from Clinical Drug Trials. Health and Human Rights Journal https://www.hhrjournal.org/2017/05/remove-the-for-profit-variable-from-clinical-drug-trials/ (2017).
- Ashrafian, H., Patel, V. M., Skapinakis, P. & Athanasiou, T. Nobel Prizes in medicine: are clinicians out of fashion? J R Soc Med 104, 387–389 (2011).
- Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D. G., Ntzani, E. & Ioannidis, J. P. A. Translation of highly promising basic science research into clinical applications. Am. J. Med. 114, 477–484 (2003).
- Alfred Nobel’s health and his interest in medicine. NobelPrize.org https://www.nobelprize.org/alfred-nobel/alfred-nobels-health-and-his-interest-in-medicine/.
- Athinarayanan, S. J. et al. Long-Term Effects of a Novel Continuous Remote Care Intervention Including Nutritional Ketosis for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A 2-Year Non-randomized Clinical Trial. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10, 348 (2019).
- DONG, T. A. et al. Intermittent Fasting: A Heart Healthy Dietary Pattern? Am J Med 133, 901–907 (2020).
- van Namen, M., Prendergast, L. & Peiris, C. Supervised lifestyle intervention for people with metabolic syndrome improves outcomes and reduces individual risk factors of metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 101, 153988 (2019).
- Kord-Varkaneh, H. et al. The Influence of Fasting and Energy Restricting Diets on Blood Pressure in Humans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 27, 271–280 (2020).
- Mittal, M., Siddiqui, M. R., Tran, K., Reddy, S. P. & Malik, A. B. Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 20, 1126–1167 (2014).
- van der Vliet, A. & Janssen-Heininger, Y. M. W. Hydrogen peroxide as a damage signal in tissue injury and inflammation: murderer, mediator, or messenger? J Cell Biochem 115, 427–435 (2014).
- Circu, M. L. & Aw, T. Y. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 48, 749–762 (2010).
- Khomich, O. A., Kochetkov, S. N., Bartosch, B. & Ivanov, A. V. Redox Biology of Respiratory Viral Infections. Viruses 10, (2018).
- Cheng, R. Z. Can early and high intravenous dose of vitamin C prevent and treat coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19)? Medicine in Drug Discovery (2020).
- Schönrich, G., Raftery, M. J. & Samstag, Y. Devilishly radical NETwork in COVID-19: Oxidative stress, neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), and T cell suppression. Adv Biol Regul 77, 100741 (2020).
- Delgado-Roche, L. & Mesta, F. Oxidative Stress as Key Player in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) Infection. Arch Med Res 51, 384–387 (2020).
- Zarbafian, M., Dayan, S. & Fabi, S. G. Teachings from COVID-19 and aging-An oxidative process. J Cosmet Dermatol (2020) doi:10.1111/jocd.13751.
- How to Avoid Getting Sick When You’re Around People All Day. Washingtonian https://www.washingtonian.com/2016/01/15/how-to-avoid-getting-sick-when-youre-around-people-all-day/ (2016).
- Levy, T. Primal Panacea. (MedFox Publishing).
- Levy, T. & 成长. 万应灵丹: 关于维生素C的百科全书. in (Kindle Publisher, 2017).
- Wang, Y. et al. Effects of vitamin C and vitamin D administration on mood and distress in acutely hospitalized patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 98, 705–711 (2013).
- Hemilä, H. Vitamin C and Infections. Nutrients 9, (2017).
- Hemilä, H. & Chalker, E. Vitamin C may reduce the duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients: a meta-regression analysis. J Intensive Care 8, 15 (2020).
- Sawyer, M., Mike, J. & Chavin, K. Antioxidant therapy and survival in ARDS (abstract). Crit Care Med (1989).
- Marik, P. E., Khangoora, V., Rivera, R., Hooper, M. H. & Catravas, J. Hydrocortisone, Vitamin C, and Thiamine for the Treatment of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock: A Retrospective Before-After Study. Chest 151, 1229–1238 (2017).
- Cheng, Richard Z. Preliminary Report of Chinese High Dose Vitamin C for Covid-19 Treatment Studies.
- Kim, T. K., Lim, H. R. & Byun, J. S. Vitamin C supplementation reduces the odds of developing a common cold in Republic of Korea Army recruits: randomised controlled trial. BMJ Mil Health (2020) doi:10.1136/bmjmilitary-2019-001384.
- Carr, A. C. et al. Hypovitaminosis C and vitamin C deficiency in critically ill patients despite recommended enteral and parenteral intakes. Crit Care 21, 300 (2017).
- de Grooth, H.-J. & et al. Early plasma vitamin C concentration, organ dysfunction and ICU mortality. Intensive Care Medicine 40, (2014).
- Vincent, J. L. et al. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med 22, 707–710 (1996).
- ‘Unusual’ IV High-Dose Vitamin C Success Story in COVID-19 | MedPage Today. https://www.medpagetoday.com/casestudies/infectiousdisease/87976.
- Chiscano-Camón, L., Ruiz-Rodriguez, J. C., Ruiz-Sanmartin, A., Roca, O. & Ferrer, R. Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care 24, 522 (2020).
- NIH PDQ. High-Dose Vitamin C (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version – National Cancer Institute. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/cam/hp/vitamin-c-pdq.
- Cheng, R. Covid-19 Presentations. drwlc.com http://www.drwlc.com/Covid-19_talks.shtml.
- Cheng, R., Kogan, M. & Devra, D. Ascorbate as Prophylaxis and Therapy for COVID-19—Update From Shanghai and U.S. Medical Institutions – Richard Z Cheng, Mikhail Kogan, Devra Davis, 2020. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/2164956120934768.
- Shanghai Government Officially Recommends Vitamin C for COVID-19. http://orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n16.shtml.
- Cheng, Richard. Shanghai and Guangdong Governements’ official recommendation of Vit C in Covid-19 treatment. http://www.drwlc.com/blog/2020/04/16/covid-19-vitamin-c-and-integrative-medicine-3/.
- Cheng, Richard. NIH Guest Speech: HDIVC on Covid-19. http://www.drwlc.com/Covid-19_talks.shtml.
- ITM. ITM: The Treatment to Defeat Coronavirus Pneumonia has Arrived for Early Stage Onset and Hospitalized Critically Ill ICU Patients. itmltd.com/ITM-The-Treatment-to-Defeat-Coronavirus-is-Saving-Lives-in-China-and-Beginning-to-Save-Lives-in-NYC.pdf.
- Saul, Andrew & Yanagisawa, A. Intravenous Vitamin C Treatment, Coronavirus, hospital, high doses, antiviral, vitamin C, instructions for intravenous vitamin C, Intravenous Therapy, acute viral infections, influenza, herpes zoster, common cold, rubella, mumps, idiopathic sudden hearing loss, Bell’s palsy, IVC, viral infections, Vitamin C, Magnesium sulfate, Vitamin B complex, depletion of vitamin C, therapy for sepsis, administering vitamin C intravenously, pneumonia-like virus, Riordan Clinic, Intravenous Vitamin C Protocol, cancer patients, articularly viral illnesses, peak-plasma concentration, IVC infusions, plasma vitamin C levels, Riordan protocol, IVC administration, viral diseases, hospitalization, Failure to provide intravenous vitamin C, coronavirus infection, Vitamin IVs, Right to Try Act. http://orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n07.shtml.
- Levy, T. E. COVID-19: How can I cure thee? Let me count the ways. http://orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v16n37.shtml.
- Compassionate Drug Use. https://www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/clinical-trials/compassionate-drug-use.html.