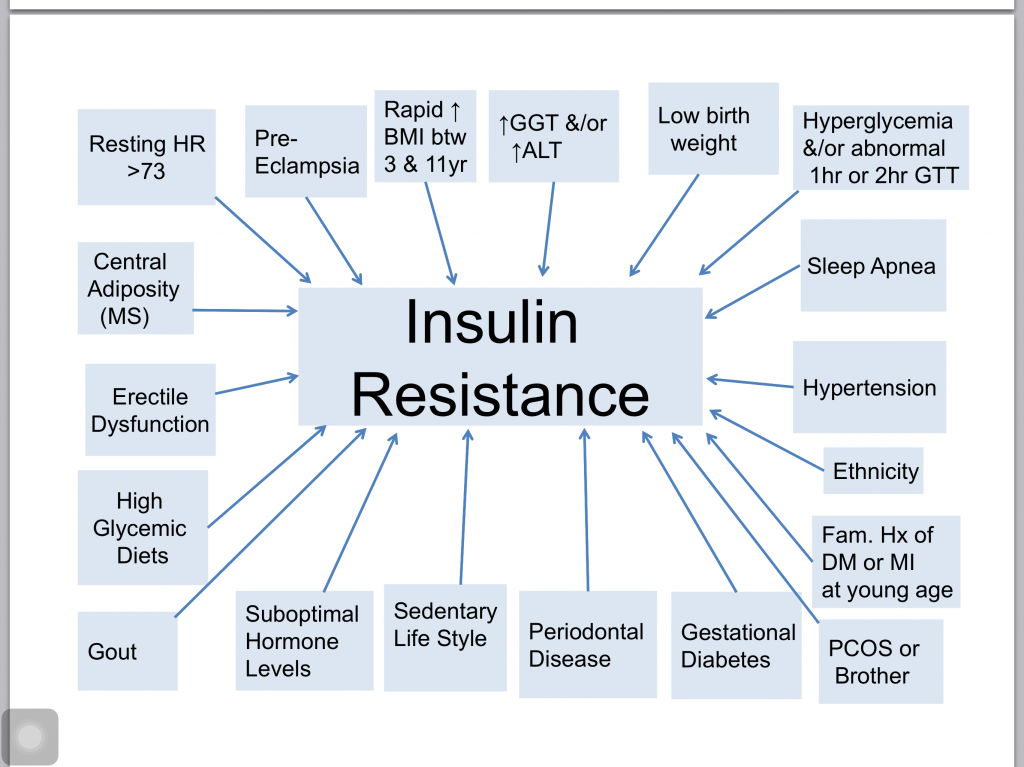
 Insulin Resistance is a proatherogenic state.
Insulin Resistance is a proatherogenic state.
Diagnosing IR:
- Moderate Elevation of GTT and ALT
- Metabolic Syndrome (also called Insulin Resistance Syndrome)
- Fasting blood sugar level: 100-125.
- TG/HDL > 3.5 (Caucasians); >3 (Mexican Americans); >2.0 (non-Hispanic Blacks).
- A1c >6.5%
- GTT is the gold standard.
- 2 Hour GTT 120-139: 66% loss of Beta cell function.
- 2 Hour GTT <140 but One hour GTT >125, high probability of IR.
- IR damages arteries regardless of blood sugar levels
- IR increases arterial inflammation
- IR immediately and progressively drives endothelia inflammation
- Majority of MI (myocardial infarction) have IR.
- Majority of ACS (acute coronary syndrome) patines are Insulin Resistant.
- IR significantly increases ischemic stroke risk in non-diabetic adults.
- GGT and ALT predict new onset DM and identify underlying IR
- These levels of GGT and AT doubled the risk:
- GGT women >/=21 units/L vs. </= 6 units/L;
- GGT men >/=47 units/L vs. </=10 units/L
- ALT women >/= 20 units/L vs. </=10 units/L
- ALT men >/= 34 units/L vs <15 units/L
- These levels of GGT and AT doubled the risk:
- Ethnicity:
- TG (triglycerides)/HDL >/= 3.5 = IR in Caucasians
- TG/HDL >/= 3.0 = IR in Mexican Americans
- TG/HDL >/= 2.0 = IR in Non-Hisanic Blacks.
- Abnormal fasting blood glucose identifies IR
- ADA definition: 100-125 mg/dl is abnormal and is a strong indicator of IR
- 2 Hour GTT:
- Increased risk for IR if >/= 125 mg/dl
- If >150, 13x greater risk of IR.
- ADA: A1c 5.7 – 6.4% = Pre-diabetes = IR
Source: Dr. Jeff Life, A4M Convention 12. 2015, Las Vegas
